Product Description
Our Products Special Features,
1) Our products passed TS16949 ISO-9001: 2000 quality management system verification
2) Material: Steel, copper, brass, aluminum, Titanium
3) Equipment: CNC lathe, CNC milling machine, CNC high-speed engraving machine, Common machines, laser engraving machines, metal injection machine
4) Precision machining capability:
5) Advanced workmanship, fitting tool, fixture, cutting tool
6) Parts can be supplied according to customers’ drawings or samples.
7) 2D/3D drawings or samples are welcome!
8). Best quality, competitive price, shortest delivery time and good service.
| Place of origin: | ZHangZhoug, China |
| Brand Name: | HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Powder Metallurgy Co.,Ltd |
| Type: | Powder metallurgy sintering |
| Surface finish | e-coating, electroplating and black oxygen |
| Measuring method | 3D system, High-lubrication, high-density and high-strength |
| Inspection equipment | Torsion test, voltage feedback test, HRC density test, lifting test and salt spray resistant test and more |
| Spare parts type: | Powder metallurgy parts |
| Machinery Test report: | Provided |
| Material: | Iron, stainless steel, copper, Alloy |
| Application: | Automotive parts, power tools, stainless steel, bushings, clutches and so many others |
| Plating: | Customized |
| After-sales Service: | Online support |
| Processing: | Powder Metallurgy, CNC Machining |
| Powder Metallurgy: | High frequency quenching, oil immersion |
| Quality Control: | 100% inspection |
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Customized Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Sintered Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Customized |
| Material: | Sintered Metal |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you calculate the gear ratio involving sun, planet, and ring gears?
The gear ratio in a planetary gear system can be calculated by considering the number of teeth on the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear. The gear ratio determines the relationship between the input speed and the output speed of the system. Here’s how you can calculate the gear ratio:
- Step 1: Count the Teeth:
Count the number of teeth on the sun gear (S), the planet gears (P), and the ring gear (R). These numbers represent the respective gear’s tooth count.
- Step 2: Determine the Gear Arrangement:
Identify the gear arrangement. In a simple planetary gear system, the sun gear is at the center, surrounded by planet gears, and enclosed by the ring gear.
- Step 3: Calculate the Gear Ratio:
The gear ratio (GR) can be determined using the formula:
GR = (R + P) / S
Where:
- R represents the number of teeth on the ring gear
- P represents the number of teeth on the planet gears (assuming they have the same number of teeth)
- S represents the number of teeth on the sun gear
The resulting gear ratio represents the speed relationship between the input and output of the planetary gear system. A gear ratio greater than 1 indicates a speed reduction, while a gear ratio less than 1 indicates a speed increase.
It’s important to note that in more complex planetary gear systems, where there are multiple sets of planet gears or additional gears, the calculation of the gear ratio may involve considering multiple gear stages and their respective tooth counts.
In summary, to calculate the gear ratio involving sun, planet, and ring gears, you need to count the teeth on each gear and use the formula (R + P) / S, where R is the number of teeth on the ring gear, P is the number of teeth on the planet gears, and S is the number of teeth on the sun gear. This calculation provides the gear ratio that defines the speed relationship between the input and output of the planetary gear system.

Can planetary gears be used in aerospace and aviation applications?
Planetary gears find extensive use in aerospace and aviation applications due to their unique characteristics and advantages. Let’s explore how planetary gears can be utilized in the aerospace and aviation industry:
- Aircraft Engines:
Planetary gears play a crucial role in aircraft engines, especially in the reduction gearbox. The reduction gearbox connects the high-speed turbine shaft with the low-speed propeller shaft, allowing efficient power transmission while maintaining optimal propeller speed. Planetary gears within the reduction gearbox help achieve the required gear ratios and torque conversion, ensuring smooth and reliable engine operation.
- Landing Gear Systems:
Planetary gears are also utilized in landing gear systems of aircraft. These gears provide the necessary torque and force to retract and extend the landing gear during takeoff and landing. Planetary gears offer compactness, high torque capacity, and the ability to handle heavy loads, making them suitable for this critical application.
- Actuation Systems:
Actuation systems in aerospace and aviation, such as those used for flight control surfaces, also benefit from the use of planetary gears. These gears enable precise and reliable movement of control surfaces, such as ailerons, elevators, and rudders. Planetary gears’ ability to handle high torques, provide accurate positioning, and withstand varying loads makes them well-suited for actuation systems.
- Satellite and Spacecraft Mechanisms:
In satellite and spacecraft applications, planetary gears are utilized in various mechanisms. They can be found in solar array drives, antenna pointing systems, and deployment mechanisms for scientific instruments. Planetary gears offer compactness, high torque transmission, and the ability to handle the extreme conditions of space environments.
- Auxiliary Power Units (APUs):
APUs in aircraft are responsible for providing auxiliary power during ground operations and in-flight emergencies. Planetary gears are often employed in APU systems to transfer power from the engine to the auxiliary systems, such as electrical generators or hydraulic pumps. These gears ensure efficient power transmission and reliable operation of the APU.
In summary, planetary gears have significant applications in aerospace and aviation. They are utilized in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, actuation systems, satellite and spacecraft mechanisms, as well as auxiliary power units. The compact size, high torque capacity, precise positioning, and reliable operation of planetary gears make them well-suited for these critical applications in the aerospace and aviation industry.
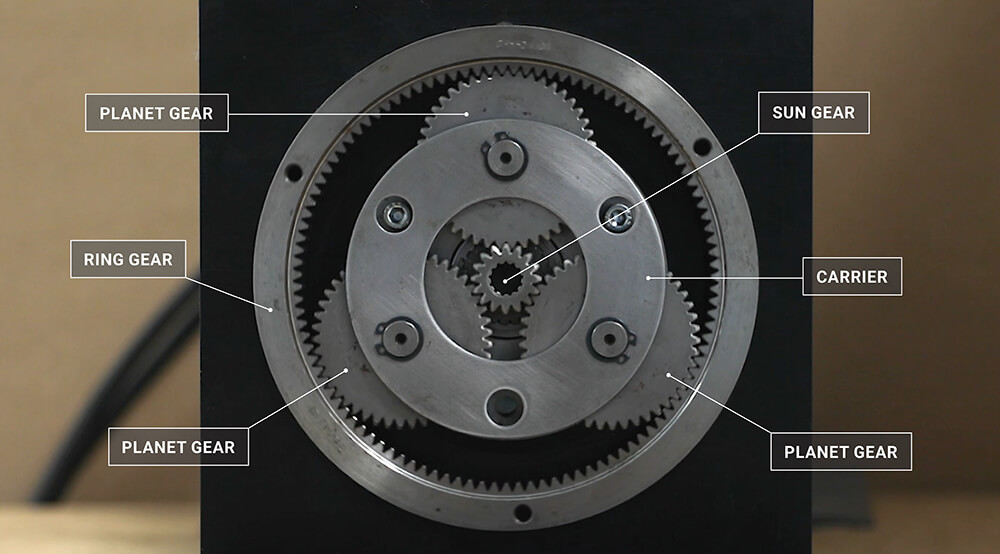
How do planetary gears differ from other types of gear arrangements?
Planetary gears, also known as epicyclic gears, possess unique characteristics and differ from other types of gear arrangements in several ways. Let’s explore the distinguishing features of planetary gears:
- Internal Gear Meshing:
Unlike other gear arrangements where the gears typically mesh externally, planetary gears have internal gear meshing. This means that the gear teeth of the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear are located on the inside surfaces, allowing for compact and space-efficient designs.
- Multiple Gear Sets:
Planetary gear systems consist of multiple gear sets working in parallel or series. These gear sets include the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear. By combining and configuring these gear sets, different gear ratios and torque distributions can be achieved, providing versatility and flexibility in various applications.
- Central Sun Gear:
A distinctive feature of planetary gears is the presence of a central sun gear. The sun gear is typically driven by an input source, such as a motor or engine. It is located at the center of the gear arrangement and serves as the primary driver for overall gear operation.
- Orbiting Planet Gears:
In planetary gears, the planet gears rotate on their own axes while simultaneously orbiting around the sun gear. This combination of rotational and orbital movement allows for efficient torque transmission and enables the gear arrangement to achieve different gear ratios based on the relative sizes and positions of the gears.
- Compact Size:
One of the key advantages of planetary gears is their compact size. The internal gear meshing and the arrangement of multiple gear sets within a single gear system contribute to their space-saving design. This makes planetary gears suitable for applications where size and weight restrictions are important considerations.
- Wide Range of Applications:
Planetary gears find applications in various industries and mechanical systems. They are commonly used in automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, robotics, aerospace systems, and more. Their ability to achieve different gear ratios, transmit torque efficiently, and operate in compact spaces makes them versatile solutions in diverse engineering applications.
In summary, planetary gears differ from other types of gear arrangements due to their internal gear meshing, multiple gear sets, central sun gear, orbiting planet gears, compact size, and wide range of applications. These characteristics make planetary gears suitable for achieving various gear ratios, transmitting torque efficiently, and meeting the space requirements of different mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2023-09-28